NASA says astronomers discovered a “rapidly developing black hole” in the early universe.
This finding might help us grasp the relationship between the earliest supermassive black holes and young galaxies.
Using data from the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers discovered a fast-developing black hole in the early cosmos that is regarded as a vital “missing link” between young star-forming galaxies and the first supermassive black holes.
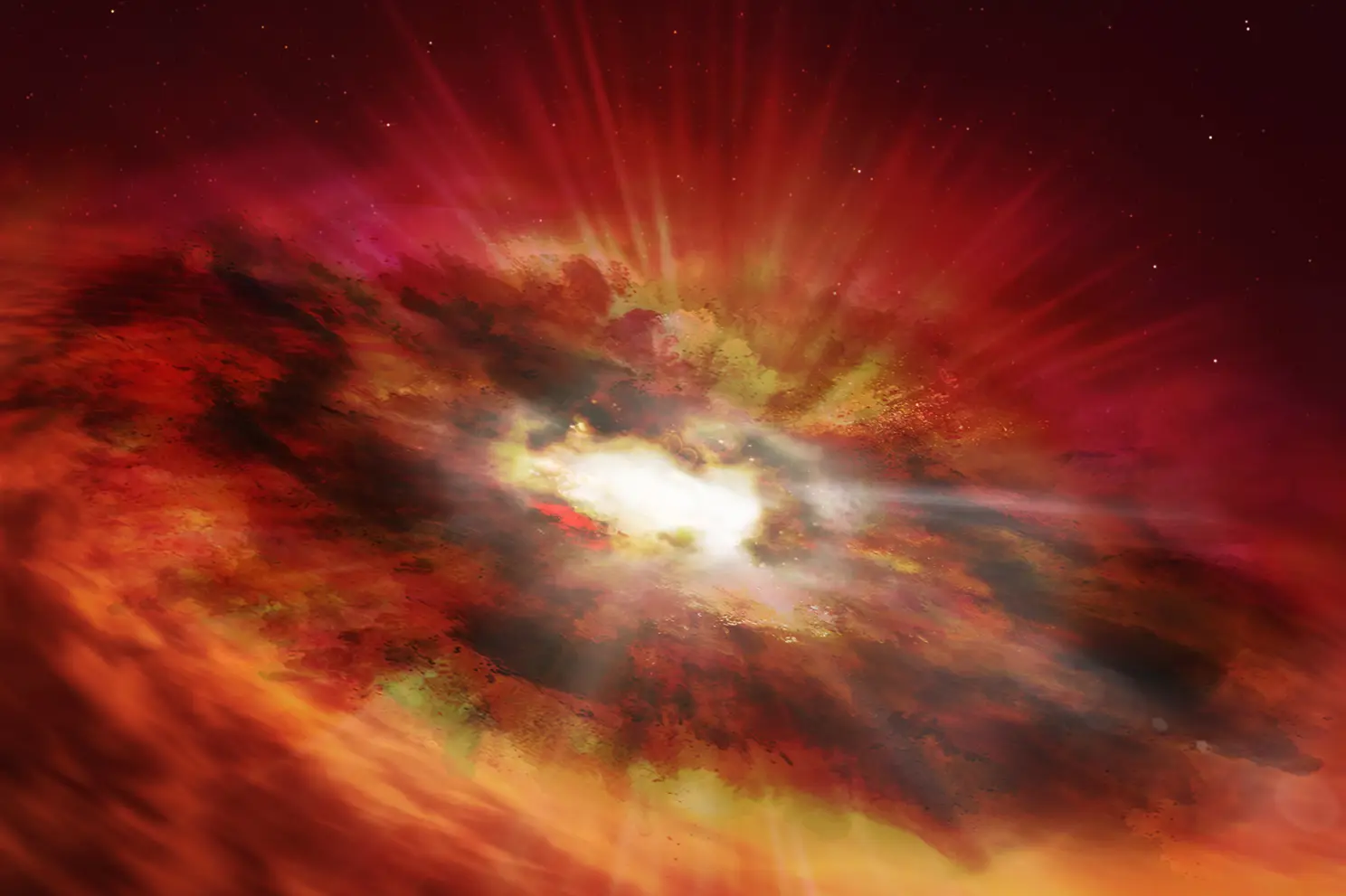
The US space agency also published an artist’s rendition of a supermassive black hole and a Hubble Space Telescope photograph.
“This artist’s impression is of a supermassive black hole within the dust-shrouded core of a furious starburst galaxy,” NASA said.
“Once the dust is gone, it will become an incredibly brilliant quasar.
It was discovered in a Hubble deep-sky study barely 750 million years after the Big Bang.
Quasars are very luminous cosmic objects driven by black holes.
NASA calls the black hole GNz7q a “monster” that has been lurking in a well-studied part of the sky.
Black holes are thought to originate in dusty starburst galaxies before becoming quasars.
GNz7q is a “missing link” that might assist prove the idea.
The black hole is reported to be 750 million years old.
The cosmos is estimated to be 14 billion years old.
“Our study implies that GNz7q is the first example of a rapidly expanding black hole in the dusty core of a starburst galaxy at an age close to the first supermassive black hole known in the universe,” said lead author Seiji Fujimoto.
“The object’s characteristics throughout the electromagnetic spectrum match theoretical calculations perfectly.”
It “provides a new path toward understanding the fast emergence of supermassive black holes in the early cosmos,” Fujimoto added.
In addition, “our finding shows the existence of progenitors to supermassive black holes.”